Pneumatic mobility
Graduation project, 2020
Spatial design, Industrial design
Once autonomous vehicles become widespread, the hardware of mobility will also change. For instance, Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene (ETFE), currently in use in architecture, can be implemented to create autonomous cars whose cabins fold flat when driving without passengers to minimize visual footprint, and expand to form a small room-like space when stationary. Using this technology, a new camping system can be designed for natural parks. When autonomous vehicles holding passengers dock at a base camp, the individual vehicles become separate rooms, and the base camp becomes a communal space. With this system, tourists can enjoy camping in nature without the need to find lodging or transportation.
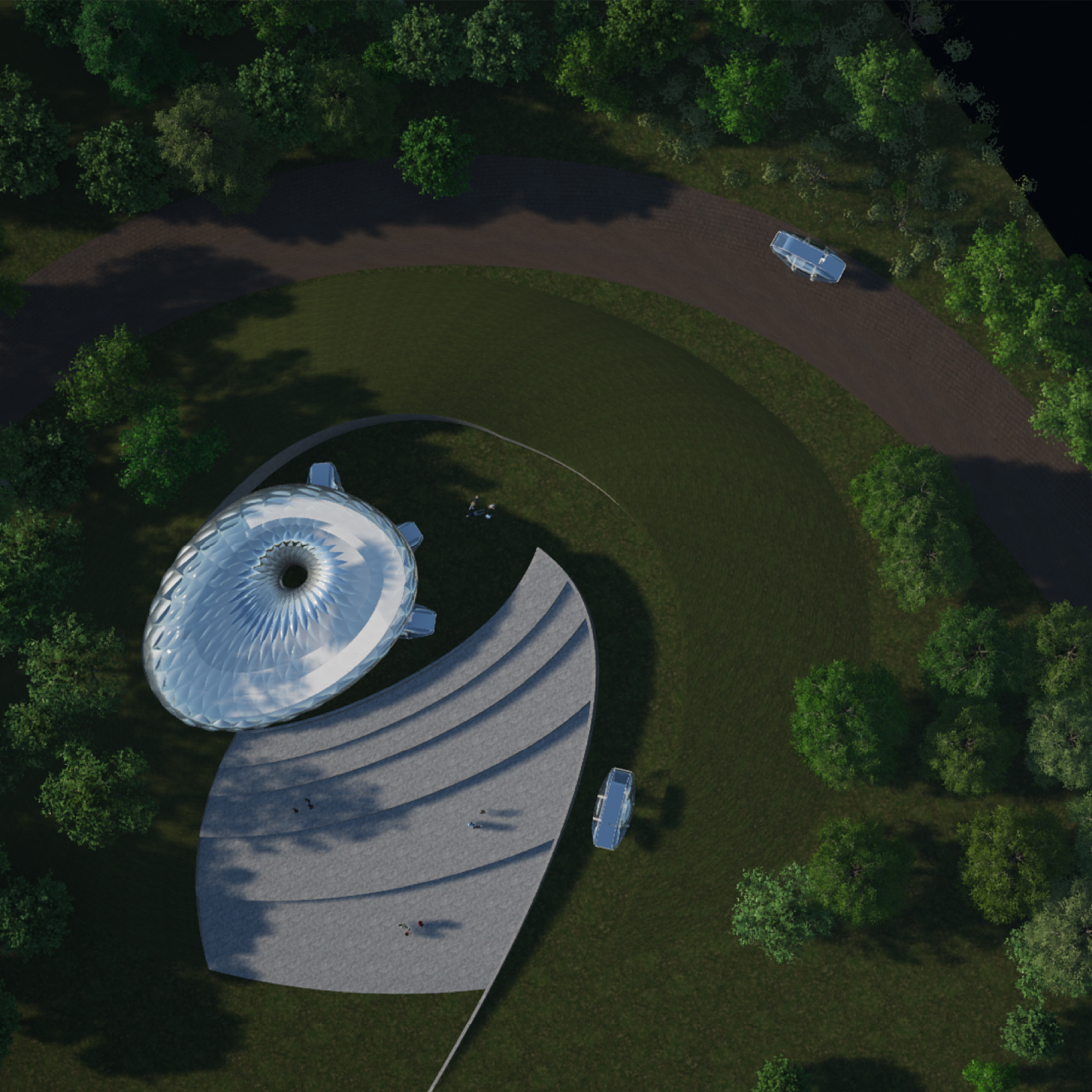

In a future where autonomous driving is common, new systems will emerge to meet both the growing importance of environmental protection and the demand for enjoying nature. This is a new type of camping that prevents accidental and intentional destruction of nature caused by free camping and allows you to enjoy nature while using the autonomous driving system. A new type of autonomous mobility hardware is important for this.

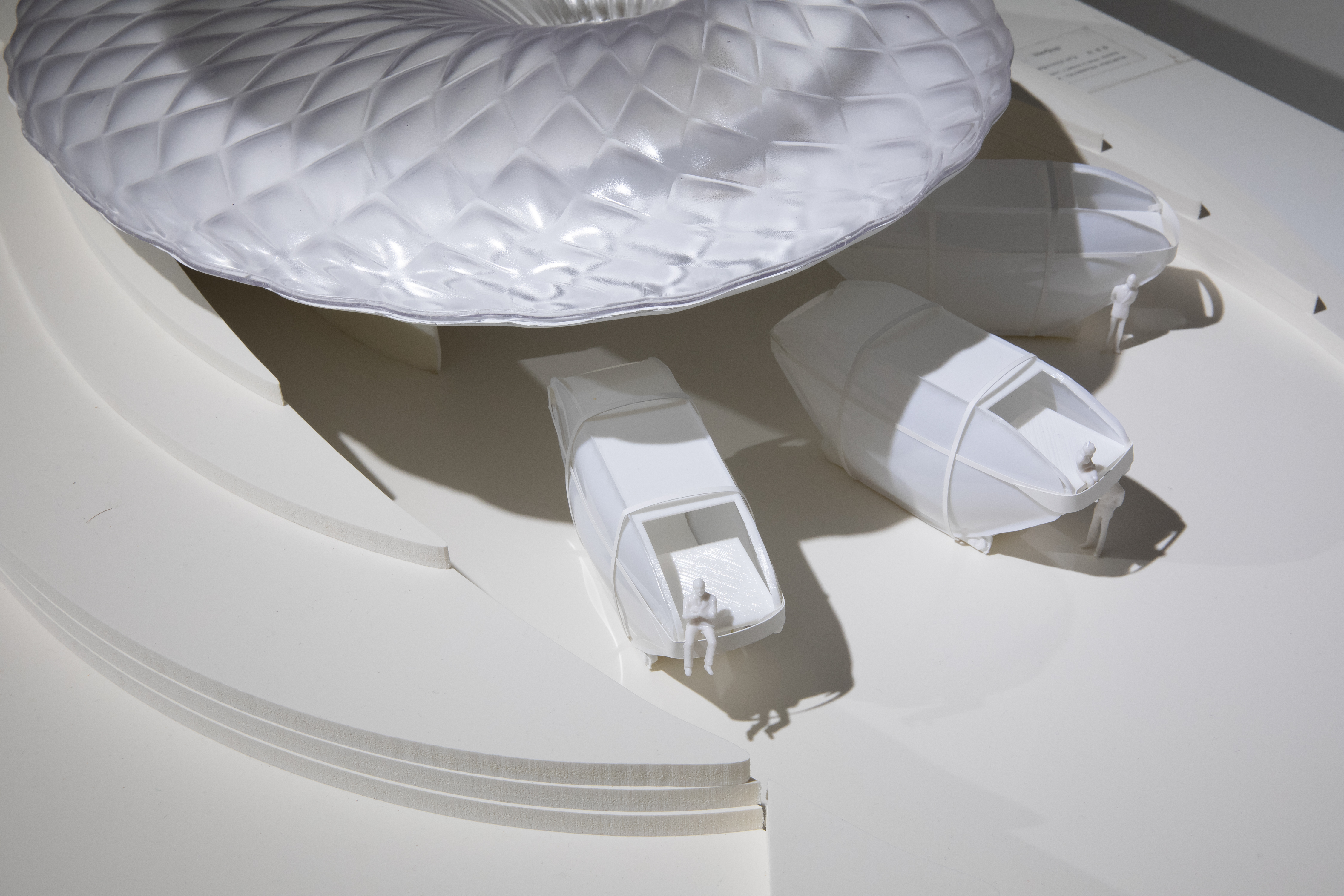
The autonomous driving module that changes the nature of space with a pneumatic structure
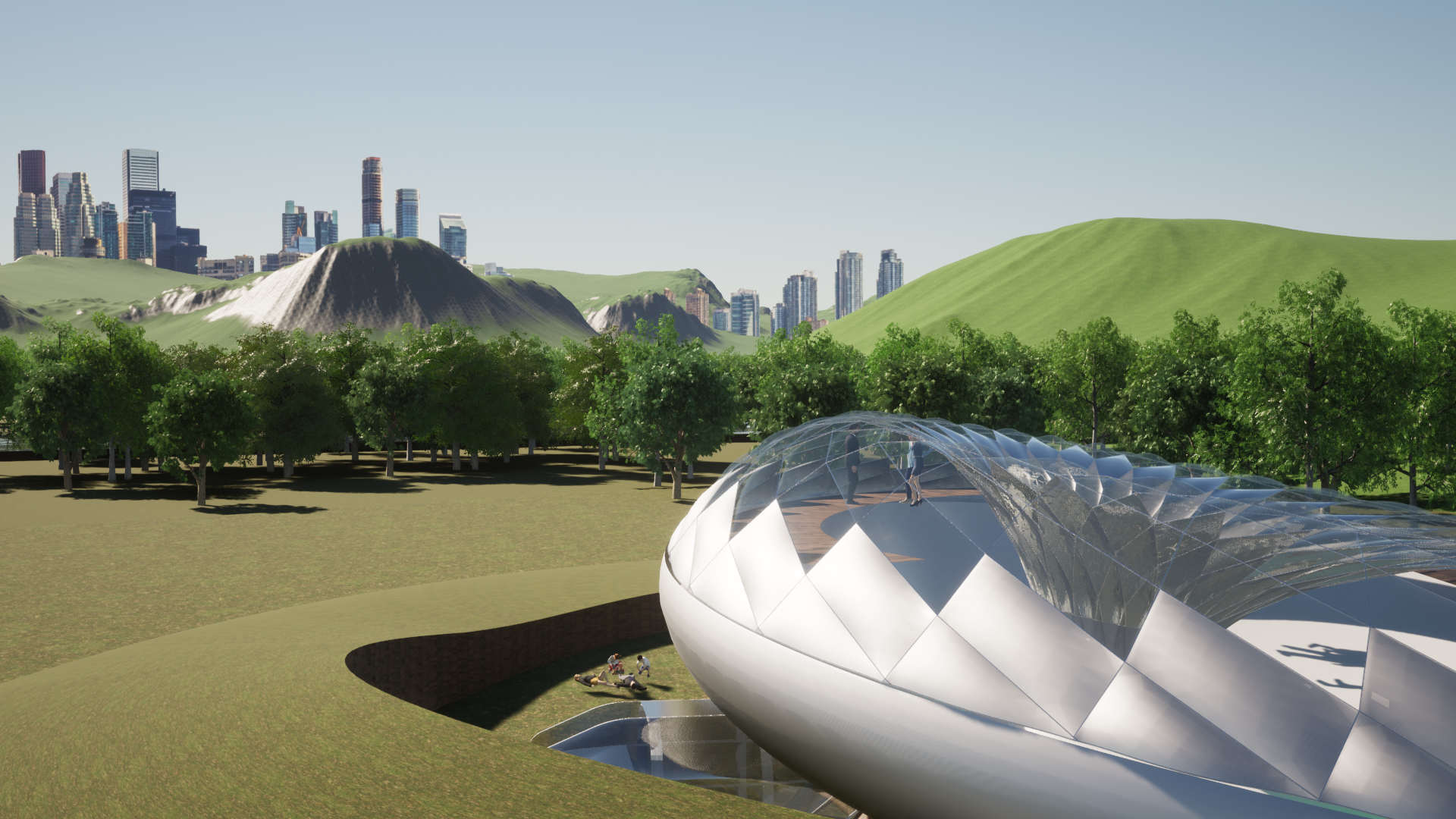
A new type of autonomous driving mobility uses a pneumatic structure to quickly drive in a flat shape when a person is on board, and expands when a person is on board, providing a comfortable space. In addition, all sides are transparent, reducing motion sickness and ensuring light and visibility. This will lower the height of the vehicle for occupantless mobility, allowing passengers in other mobility to pass without obstructing the view.
User scenario
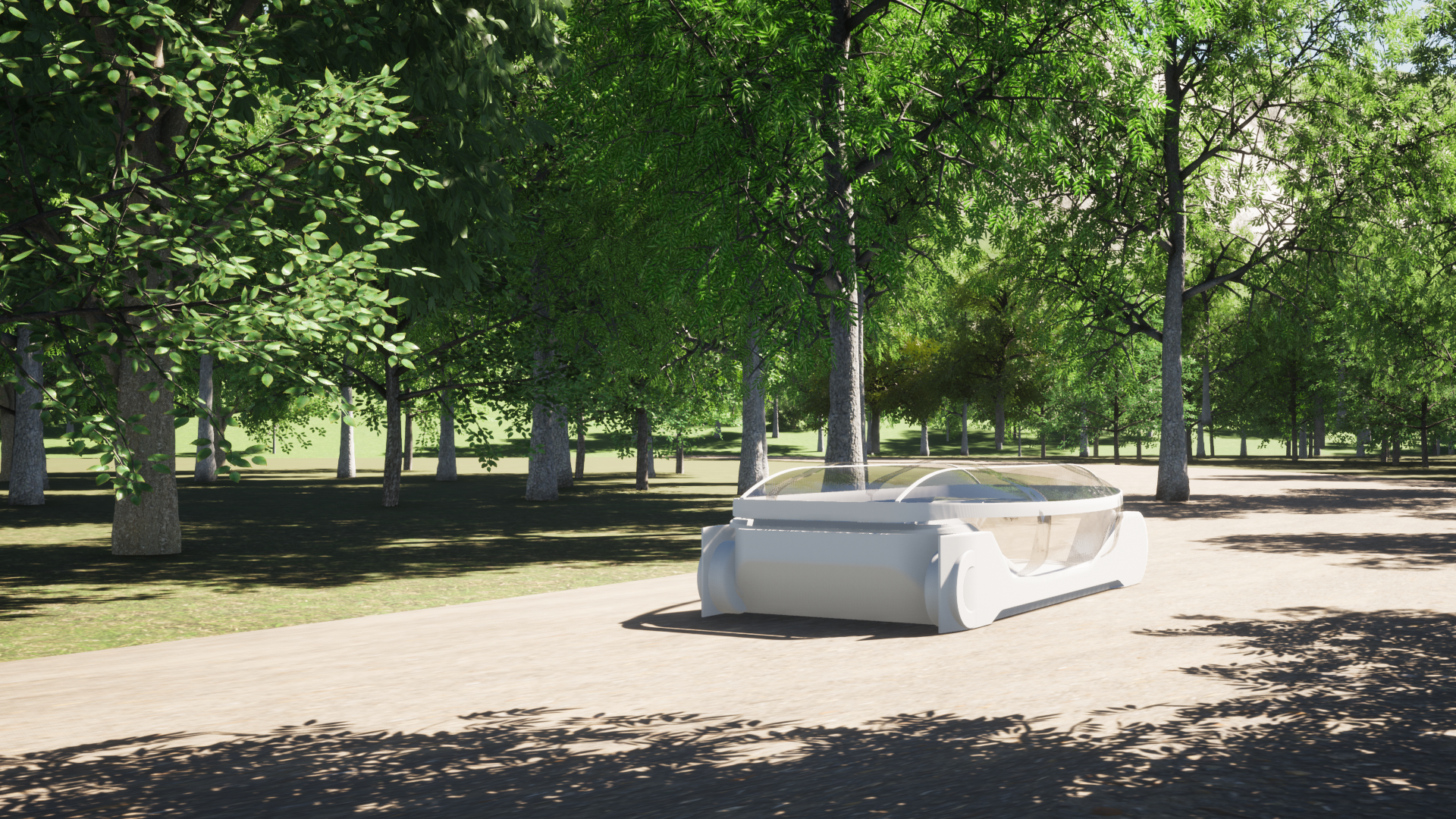 1. Self-driving mobility will autonomously drive to the place where there are spectators to board.
1. Self-driving mobility will autonomously drive to the place where there are spectators to board.

2. Visitors wait for mobility at their location rather than at a bus stop before boarding. In addition, Autonomous Mode Mobility has a low ride height so that it does not block the view of passengers in spectator mode.
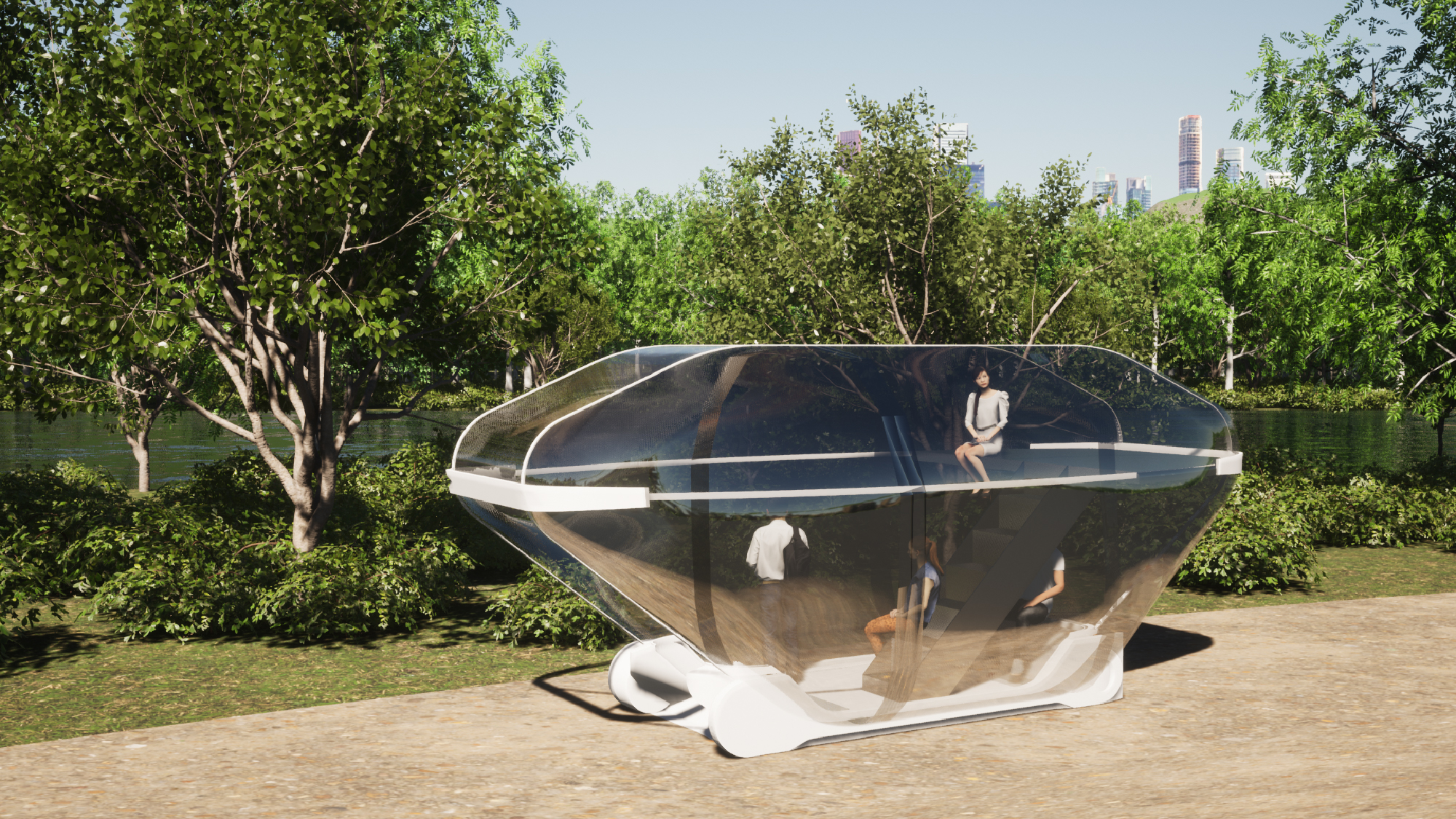

3. Mobility in viewing mode operates at around 10km/h to view the scenery, and since it is driving at low speed, you can climb the deck on the 2nd floor to enjoy the scenery.
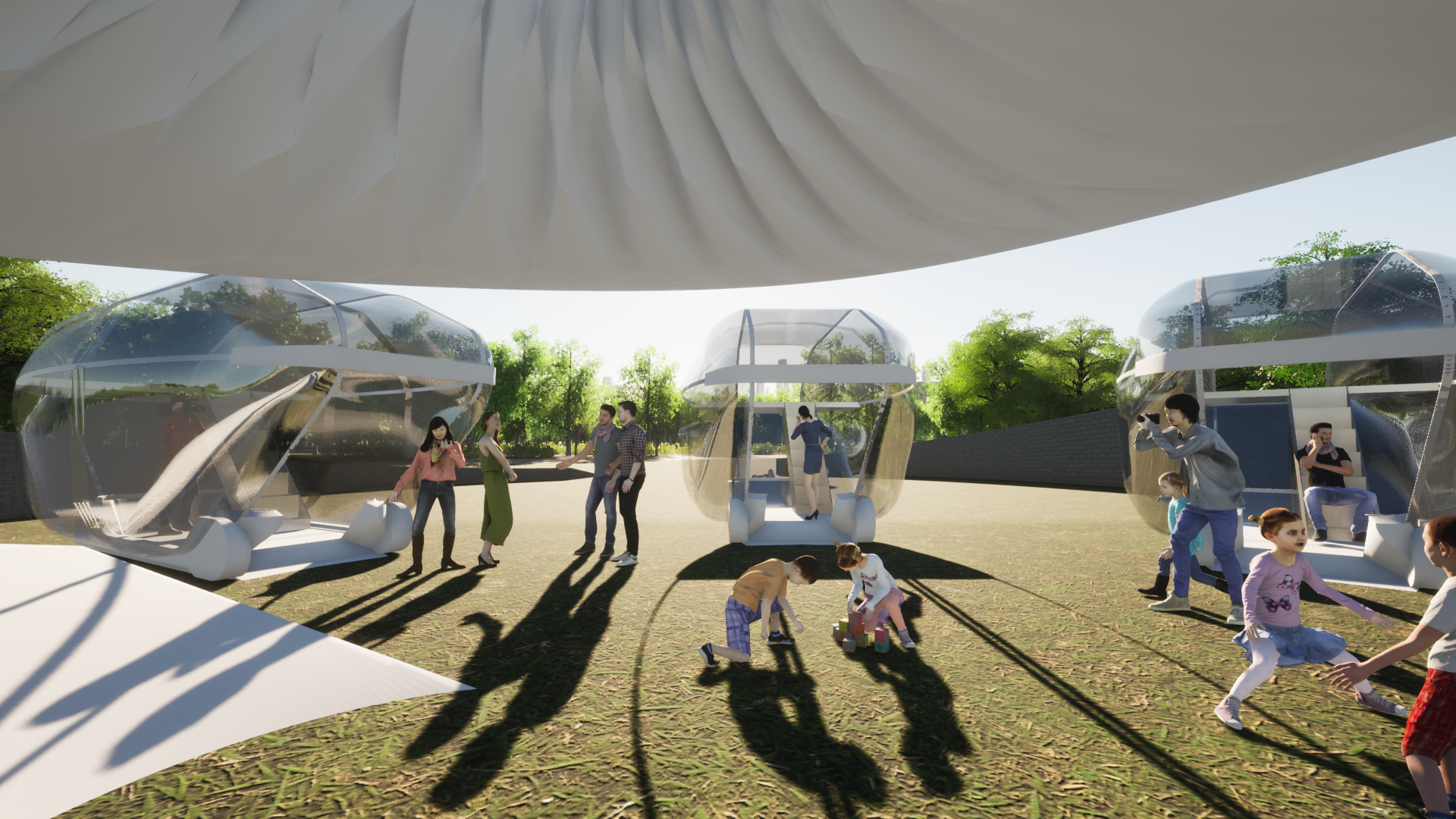

4. A mobility can make up to 5 stops, and a stopped mobility works as a single room.

5. The inside of the viewing camp has a spiral three-story structure that can hold small exhibitions.
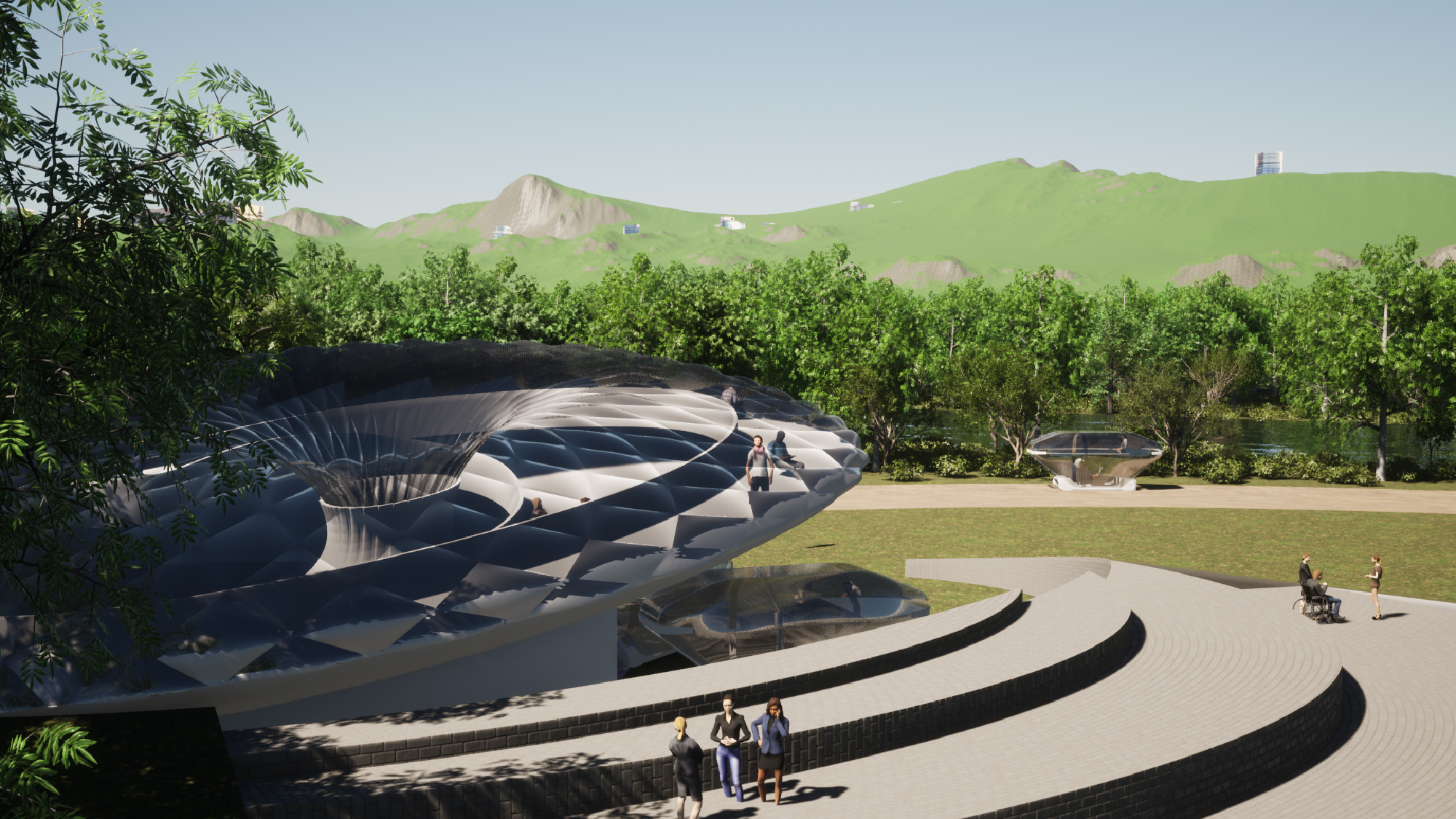
6. Visitors can freely enjoy nature both inside and outside the camp.
Process
Research



Expansion of pneumatic mobility

Scalability of pneumatic mobility
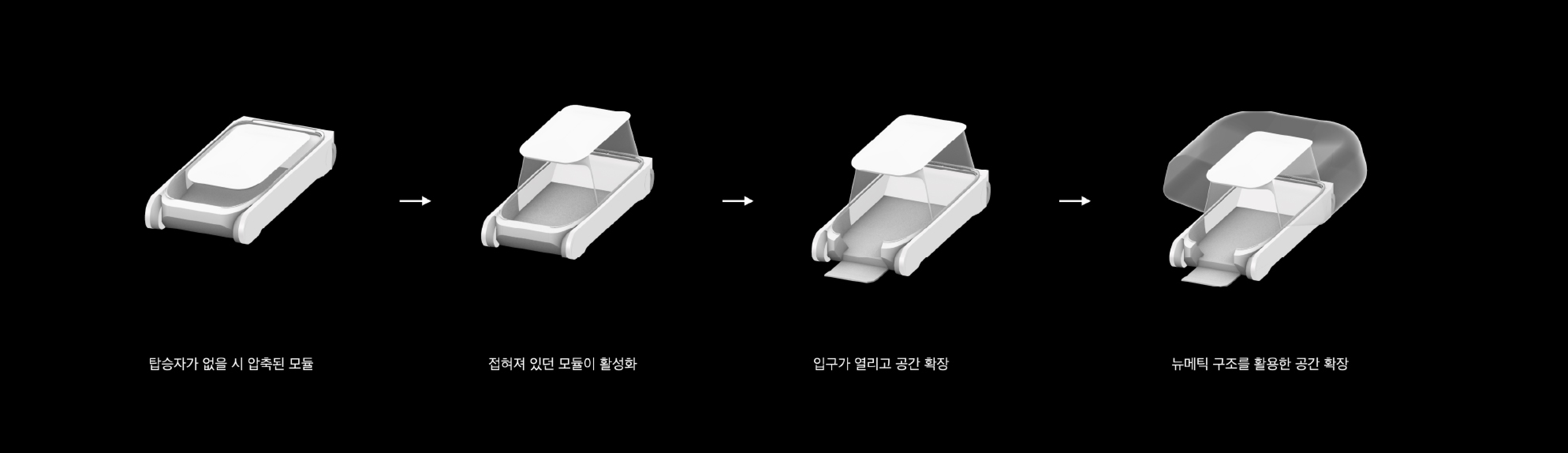
Expandability of the space constituted by pneumatic mobility
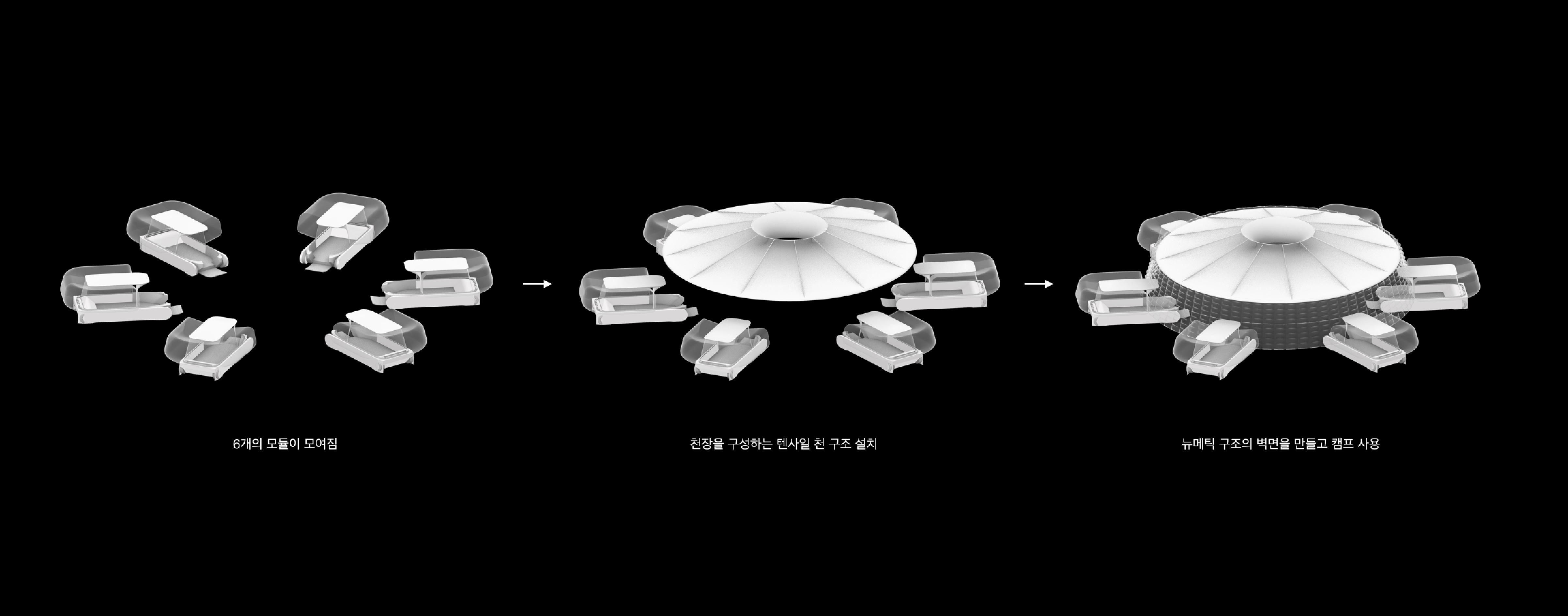
Variation in the way pneumatic mobility forms spaces
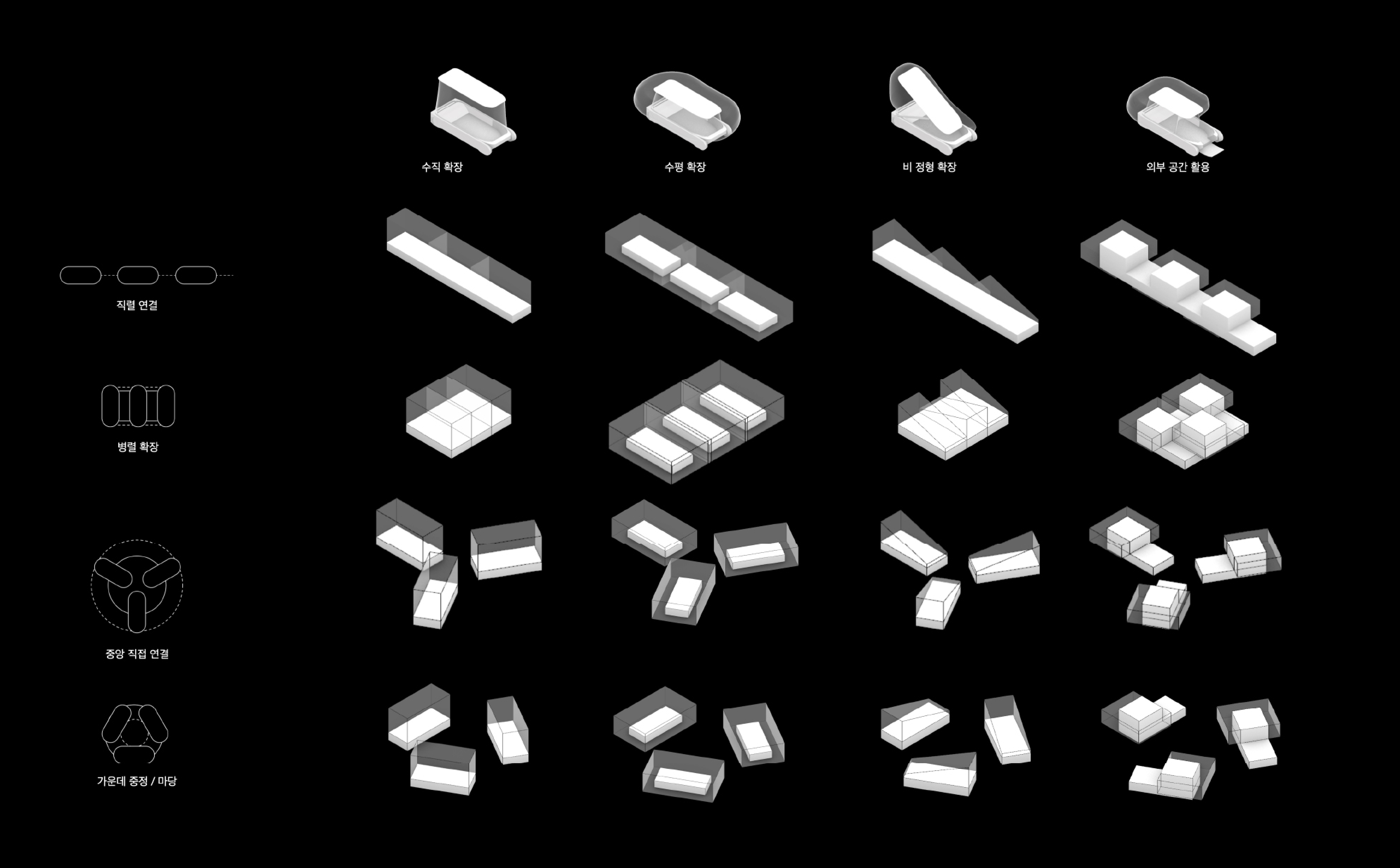
Draft
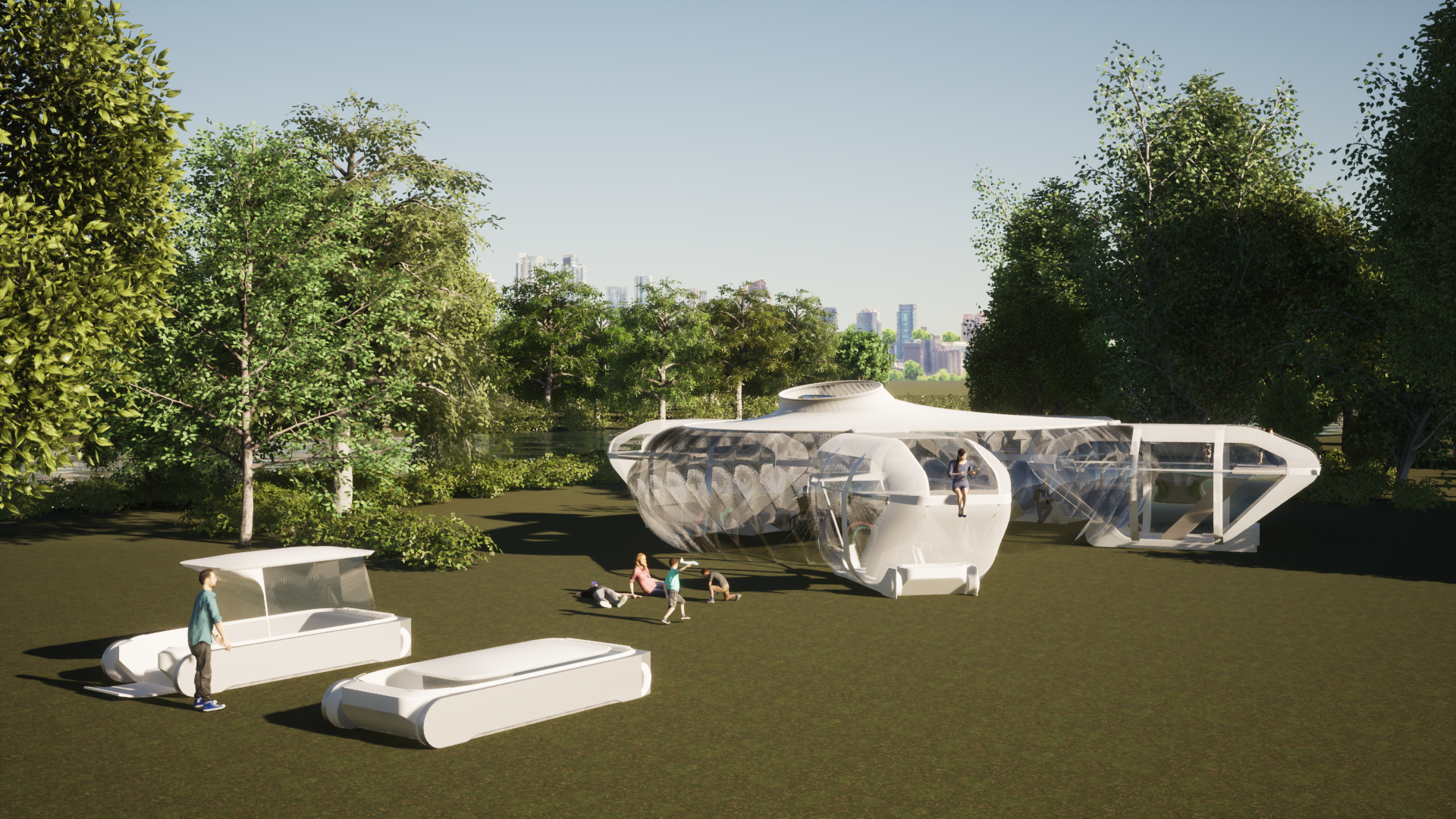
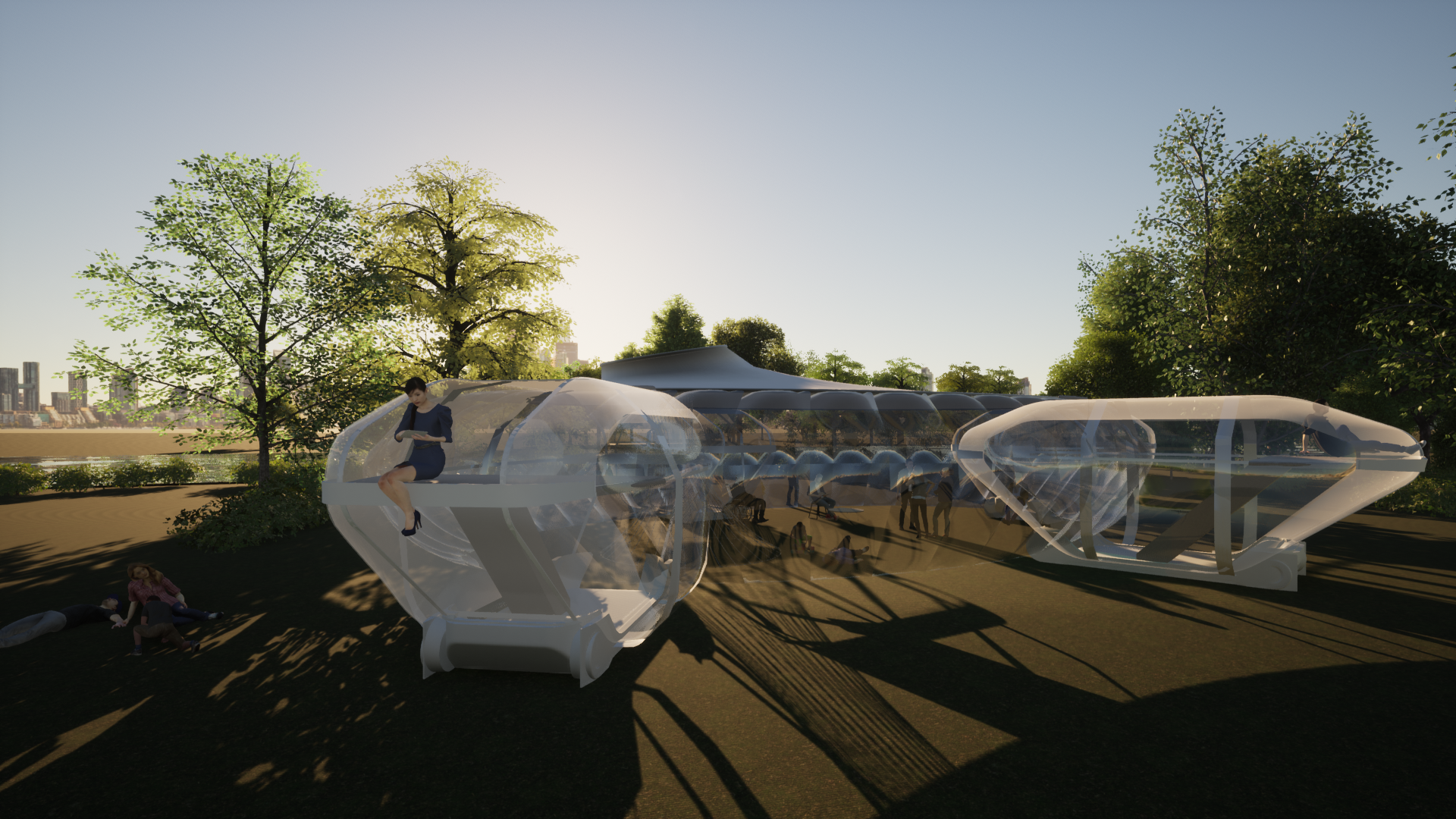



parametric design
Model making - Vacuum molding
Graduation show